Analyzing data with correlations worksheet answers psychology – In the realm of psychology, analyzing data with correlations plays a pivotal role in uncovering relationships and patterns. This comprehensive guide, “Analyzing Data with Correlations: Worksheet Answers for Psychology,” delves into the intricacies of correlation analysis, providing a thorough understanding of its types, methods, and applications within the field.
Correlations, as statistical measures, quantify the strength and direction of associations between variables. Understanding these associations is crucial for psychologists to draw meaningful conclusions from research data and advance our understanding of human behavior.
1. Introduction: Analyzing Data With Correlations Worksheet Answers Psychology
Analyzing data with correlations is a crucial aspect of psychological research, providing valuable insights into the relationships between variables and helping researchers understand complex psychological phenomena.
Correlations are used to quantify the strength and direction of associations between two or more variables. By examining correlations, researchers can determine whether variables are positively or negatively related, and to what extent they influence each other.
2. Types of Correlations
Positive Correlation
A positive correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable also tends to increase. For example, a positive correlation between age and income suggests that as people get older, they tend to earn more money.
Negative Correlation
A negative correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable tends to decrease. For example, a negative correlation between stress and well-being suggests that as stress levels increase, well-being tends to decrease.
Linear Correlation
A linear correlation indicates that the relationship between two variables is linear, meaning that the data points form a straight line when plotted on a graph.
Nonlinear Correlation
A nonlinear correlation indicates that the relationship between two variables is not linear, meaning that the data points do not form a straight line when plotted on a graph.
3. Methods for Analyzing Correlations
Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient
Pearson’s correlation coefficient is a measure of linear correlation that ranges from -1 to +1. A value of -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, a value of 0 indicates no correlation, and a value of +1 indicates a perfect positive correlation.
Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient is a measure of nonlinear correlation that ranges from -1 to +1. It is used when the data is not normally distributed or when the relationship between the variables is not linear.
4. Interpreting Correlations
When interpreting correlations, it is important to consider the following guidelines:
- The magnitude of the correlation coefficient indicates the strength of the relationship between the variables.
- The direction of the correlation coefficient indicates whether the relationship is positive or negative.
- The context and limitations of the study should be taken into account when interpreting correlations.
5. Applications of Correlation Analysis in Psychology
Correlation analysis has been widely used in psychological research to advance our understanding of various psychological phenomena, including:
- Identifying risk factors for mental health disorders
- Examining the relationship between personality traits and behavior
- Studying the effects of interventions on psychological outcomes
6. Advanced Techniques for Analyzing Correlations
Partial Correlation, Analyzing data with correlations worksheet answers psychology
Partial correlation is a statistical technique used to examine the relationship between two variables while controlling for the effects of one or more other variables.
Multiple Regression
Multiple regression is a statistical technique used to predict the value of a dependent variable based on the values of two or more independent variables.
7. Ethical Considerations
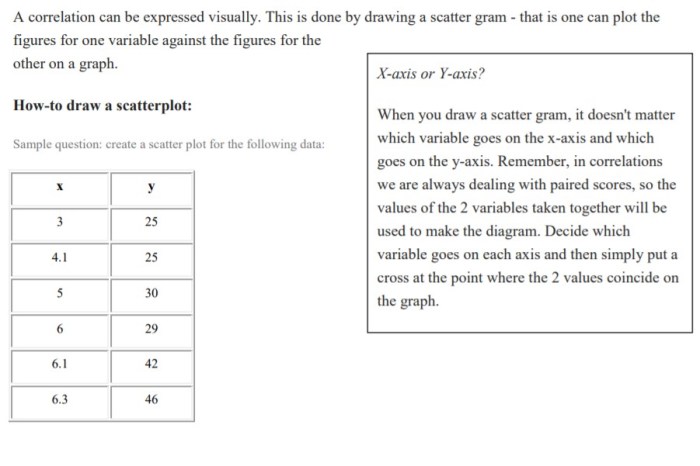
When analyzing correlations in psychology, it is important to consider the following ethical considerations:
- Transparency: Researchers should be transparent about the methods and procedures used to analyze correlations.
- Responsible reporting: Researchers should avoid making exaggerated or misleading claims about the results of correlation analyses.
Expert Answers
What are the different types of correlations?
Correlations can be positive or negative, linear or nonlinear. Positive correlations indicate a direct relationship between variables, while negative correlations indicate an inverse relationship. Linear correlations represent a straight-line relationship, while nonlinear correlations represent a curved or more complex relationship.
How do I interpret the magnitude of a correlation?
The magnitude of a correlation coefficient indicates the strength of the relationship between variables. Coefficients range from -1 to 1, with values closer to 0 indicating a weak relationship and values closer to 1 or -1 indicating a strong relationship.
What are the ethical considerations involved in analyzing correlations?
Researchers must be transparent about their methods and findings, avoiding selective reporting or misinterpretation of correlations. It is also important to consider the potential for confounding variables and ensure that correlations are not misinterpreted as causal relationships.