A dilation produces a congruent figure – Dilation, a geometric transformation, holds the power to enlarge or reduce the size of a figure while maintaining its inherent shape and proportions. This fascinating concept, known as congruence, forms the cornerstone of this exploration, revealing the intriguing properties and applications of dilation in diverse fields.
As we delve deeper into the realm of dilation, we will uncover its ability to produce congruent figures, preserving their essential characteristics. We will examine the role of the center of dilation and scale factor in shaping the transformation process.
Moreover, we will explore the practical applications of dilation in fields ranging from architecture to engineering, showcasing its versatility and significance in the world around us.
Definition of Dilation: A Dilation Produces A Congruent Figure
Dilation is a transformation that increases the size of a figure. It involves multiplying the distance of each point in the figure from a fixed point called the center of dilation by a positive scale factor. The scale factor determines the amount of enlargement or reduction.
Congruence
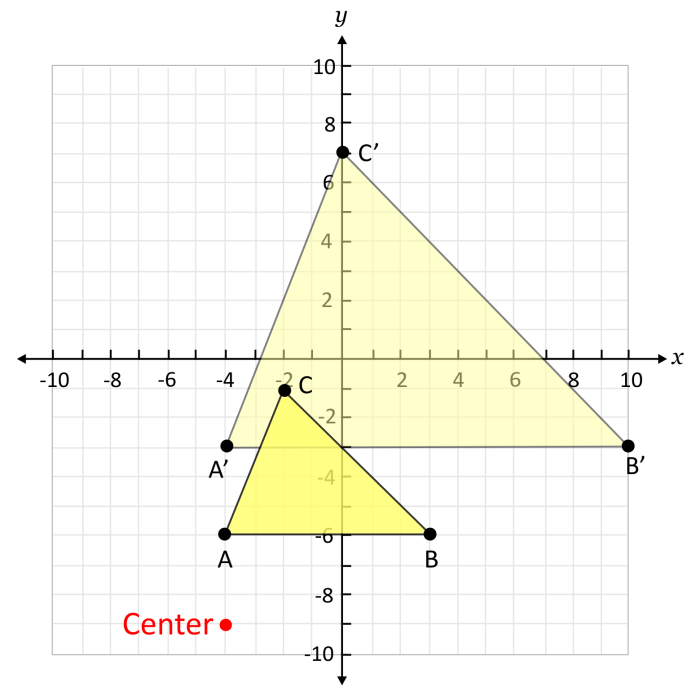
Congruence is the property of two figures having the same size and shape. Dilation can produce congruent figures if the scale factor is 1. This means that the resulting figure is the same size and shape as the original figure, but it may be located in a different position.
Properties of Dilation, A dilation produces a congruent figure
- Preservation of shape: Dilation preserves the shape of the original figure.
- Enlargement or reduction of size: Dilation can either enlarge or reduce the size of the original figure, depending on the scale factor.
- Similarity to the original figure: The dilated figure is similar to the original figure, meaning that they have the same shape but may differ in size.
Applications of Dilation
- Architecture: Dilation is used to scale blueprints and create models of buildings.
- Photography: Dilation is used to enlarge or reduce images for printing or display.
- Engineering: Dilation is used to design structures and calculate the forces acting on them.
Example of Dilation
Consider a rectangle with vertices at (2, 3), (5, 3), (5, 6), and (2, 6). If we dilate the rectangle by a scale factor of 2 with the center of dilation at the origin, the new vertices will be (4, 6), (10, 6), (10, 12), and (4, 12). The dilated rectangle is congruent to the original rectangle, but it is twice as large.
Q&A
What is the key difference between dilation and translation?
Dilation alters the size of a figure, whereas translation shifts its position without changing its dimensions.
How does the scale factor influence the dilation process?
The scale factor determines the magnitude of the enlargement or reduction, with a value greater than 1 indicating enlargement and a value less than 1 indicating reduction.
Can dilation produce figures that are not congruent to the original?
No, dilation always produces figures that are congruent to the original, as it preserves both shape and size.